

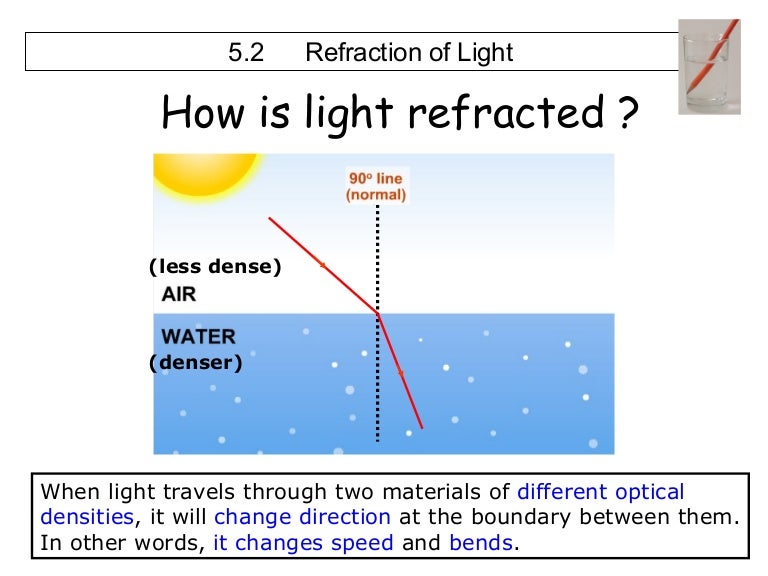
Similarly, light travels slower when moving through mediums that have higher indices of refraction. It is more difficult to move your hand through the water, and thus your hand slows down if you are applying the same amount of force. Imagine moving your hand through the air and then moving it through a body of water. In mediums that have a greater index of refraction the speed of light is less. The change in the speed of light is related to the indices of refraction of the media involved. The change in direction of the light ray depends on how the speed of light changes. As before, the angles are measured relative to a perpendicular to the surface at the point where the light ray crosses it. Why does light change direction when passing from one material ( medium ) to another? It is because light changes speed when going from one material to another.Ī ray of light changes direction when it passes from one medium to another. The speed of light is so important that its value in a vacuum is one of the most fundamental constants in nature as well as being one of the four fundamental SI units. It makes connections between space and time and alters our expectations that all observers measure the same time for the same event, for example. The speed of light varies in a precise manner with the material it traverses. The speed of light c not only affects refraction, it is one of the central concepts of Einstein's theory of relativity. Refraction: The changing of a light ray's direction (loosely called bending) when it passes through variations in matter is called refraction. This bending of light is called refraction and is responsible for many optical phenomena. In this case, the light can reach the observer by two different paths, and so the fish seems to be in two different places.
Law of Refraction: Looking at the fish tank as shown, we can see the same fish in two different locations, because light changes directions when it passes from water to air. The angles are such that our image appears exactly the same distance behind the mirror as we stand away from the mirror. When we see our reflection in a mirror, it appears that our image is actually behind the mirror - we see the light coming from a direction determined by the law of reflection. The law of reflection is very simple: The angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence. The law of reflection is illustrated in, which also shows how the angles are measured relative to the perpendicular to the surface at the point where the light ray strikes. In fact, the only way we can see an object that does not itself emit light is if that object reflects light. Large telescopes use reflections to form images of stars and other astronomical objects. When you look at the text in a book, you are actually seeing the light that is reflected from it. Whenever you look into a mirror or squint at sunlight glinting off a lake, you are seeing a reflection. reflection: the property of a propagated wave being thrown back from a surface (such as a mirror).We see the light reflected off a mirror coming from a direction determined by the law of reflection.A mirror has a smooth surface (compared with the wavelength of light) and so reflects light at specific angles.Light strikes different parts of a rough surface at different angles and is reflected, or diffused, in many different directions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
